Carbon–TiO2 hybrid dots in different configurations – optical properties, redox characteristics, and mechanistic implications†
Abstract
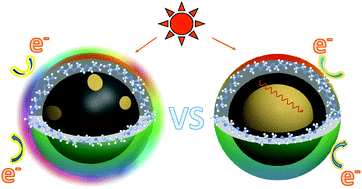
Carbon-based hybrid nanostructures, especially carbon hybrid dots with metal oxides, are important to both fundamental studies and technological applications. In this work, carbon–TiO2 hybrid dots in two different structural configurations were prepared and investigated comparatively for their optical properties and photoinduced redox characteristics, and the results suggested major differences. In the configuration of small carbon nanoparticles each coated/doped with only a small amount of TiO2, the TiO2 played the role of enhancing the surface passivation effect in conjunction with organic surface functionalization agents for the hybrid dots to exhibit a much improved performance over that of their corresponding neat carbon dots. In the other configuration, however, the hybrid dots of TiO2 nanocrystals each composited with nanoscale carbon domains were apparently similar to dye-sensitized TiO2 nanoparticle systems, with the carbon domains providing the dye function for the harvesting of visible photons. While combining nanoscale carbon and TiO2 for various applications has been a popular topic in the recent literature, the results reported here provide new insights into the different structural configurations or arrangements between the carbon and TiO2 and their associated effects on the optical and photoinduced redox properties of the hybrid nanostructures. Significant implications of the results on an understanding of the mechanistic relationships between the hybrid nano-structures/configurations and optical/redox properties are highlighted, and opportunities in the further exploration of carbon–metal oxide hybrid dots and their applications are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...