Highly efficient novel carbon monoxide gas sensor based on bismuth ferrite nanoparticles for environmental monitoring
Abstract
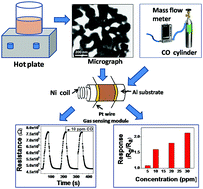
Creation of novel functionality in materials is always fascinating for researchers/scientists. Bismuth ferrite (BFO), a well known multiferroics material with simultaneous magnetic and electric order, is promising for spintronics and memory devices. Herein, we were able to demonstrate for the first time very good carbon monoxide (CO) sensing capability of bismuth ferrite (BFO) nanoparticles prepared through a simple sol–gel technique. Morphological/structural characterization was performed using various standard sophisticated modern probes, which confirms the formation of single phase BFO nanoparticles. The sensing properties of BFO nanoparticles towards CO was tested for concentrations in the range of 5 ppm–30 ppm at different temperatures (between 270 °C to 450 °C). Very good response (Rg/Ra) of around 2.12 towards 30 ppm CO at an operating temperature of 350 °C was observed. The as-prepared sensors exhibited rapid response and recovery time of around 25 s and 13 s, respectively, for sensing 30 ppm CO. In addition, the sensors are selective, highly reproducible and remain quite stable for almost 150 days, which is required for device application. A plausible mechanism has been proposed to explain the CO sensing behaviour of the BFO nanoparticles. On the basis of the observed sensing properties we believe that a BFO nanoparticle-based sensor could be a suitable alternative to conventional oxide-based sensors having various difficulties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...