Influence of redox electrolyte on the device performance of phenothiazine based dye sensitized solar cells
Abstract
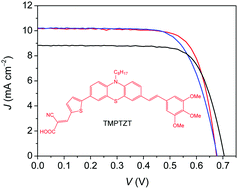
We designed and synthesized a metal-free organic sensitizer based on phenothiazine as the core moiety for application in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs). The structure of the donor–π–bridge–acceptor (D–π–A) dye 3-(5-(7-((E)-3,4,5-trimethoxystyryl)-10-octyl-10H-phenothiazin-3-yl)thiophen-2-yl)-2-cyanoacrylic acid (TMPTZT) has tri-methoxy phenyl as a donor segment on a phenothiazine core and cyanoacrylic acid as an acceptor group. In this study, we investigated the influence of iodide/triiodide and Co(bpy)32+/3+ complexes as redox electrolytes on the DSC device performance. The maximal monochromatic incident photon to current conversion efficiency (IPCE) reached a value of 70%. The solar light to electrical energy conversion efficiency of the devices with a volatile solvent based iodide/triiodide electrolyte reached up to 5.1% at AM 1.5G illumination, whereas the devices with Co(bpy)32+/3+ and ionic liquid electrolytes showed efficiencies of 4.9% and 4.5%, respectively. The DSC devices were characterized using charge extraction and Voc decay techniques to understand the difference in the photovoltaic performance of this metal free organic dye with these three types of redox electrolytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...