Template-free H-dimer and H-aggregate formation by dimeric carbocyanine dyes†
Abstract
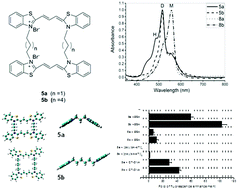
The self-organization, solvatochromism and biomolecular-interaction of cyanine dyes have been the focus of substantial research. In recent years, the DNA templated assembly of cyanine dyes has emphasized the cooperative and controlled nature of such aggregation. In this work, we explore the spontaneous and template-free self-assembly of two symmetrical dimeric carbocyanine dyes. UV-visible spectroscopy of the aggregates reveals a correlation between the alkyl linker length and the propensity of dyes to dimerize in solution. In contrast to their monomeric counterparts, dimeric trimethine dyes exhibit a superior ability to form H-dimers and H-aggregates at micromolar dye concentrations. Further, since the fluorescence of H-dimers and H-aggregates is quenched, we examine the interaction of these aggregates with biomolecules based on the possibility of de-aggregation induced fluorescence enhancement. The hexyl-linked dimeric cyanine dye exhibits more than 100-fold enhancement of fluorescence in the presence of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA). In contrast, the interaction of the same dye with [poly(dA–dT)]2 results in a decrease in fluorescence. These results highlight the tunability of self-aggregation of dimeric cyanine dyes as well as their ability to report specific interactions with biomolecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...