In vitro inhibition of Helicobacter pylori and interaction studies of lichen natural products with jack bean urease†
Abstract
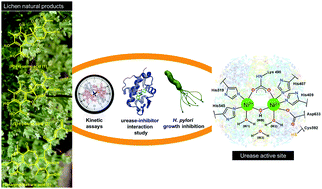
The interaction of (S)-(−)-usnic acid (2) and fumarprotocetraric acid (3), isolated from Cladonia rappii (lichen), and commercial (R)-(+)-usnic acid (1) with urease was investigated in vitro by molecular spectroscopy at pH 7.4 and kinetics experiments using jack bean type III urease. All lichen compounds tested interact with urease by a statistical quenching mechanism forming non-fluorescent complexes that change the native protein structure. Formation of complexes was spontaneous and stabilized mainly by electrostatic forces, in which the interaction magnitude was determined to be 3 < 2 < 1. Compound 2, whose tridimensional structure is disclosed here, acts as a mixed inhibitor while compounds 1 and 3 function as competitive ones. The (R)-(+)-UA (1) is the most efficient lichen metabolite with respect to impairment of the growth of five H. pylori strains. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) for the lichen metabolites tested were lower (from 2- to 7.8-fold) than those of omeprazole (reference drug) against all H. pylori strains tested. Overall, the lichen metabolites 1–3 are promising lead compounds for the design of more efficient urease inhibitors for the treatment of H. pylori infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...