An efficient microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of high-quality CuInZnS/ZnS quantum dots
Abstract
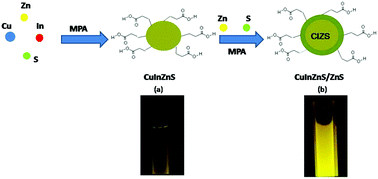
In this study, we proposed a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method to synthesize novel CuInZnS/ZnS quantum dots (QDs). As newly emerging nanoparticles, CuInZnS QDs have a low quantum yield and poor chemical stability, which limit the further bioanalysis and imaging application of CuInZnS QDs. Therefore, we used an efficient microwave-assisted hydrothermal method to synthesize high-quality CuInZnS/ZnS QDs with a high quantum yield and good chemical stability. On the surface of CuInZnS QDs, the ZnS shell was coated for the QD surface passivation, which could reduce the QD, surface defects. As a result, the fluorescence properties and quantum yield of CuInZnS/ZnS QDs have been improved significantly. This new microwave-assisted hydrothermal method possesses several features: (i) the CuInZnS/ZnS QDs thus produced have a high quantum yield (23%) and good chemical stability (more than two weeks). (ii) The CuInZnS/ZnS QDs show lower toxicity and better biocompatibility than other traditional QDs. Then, we could synthesize multi-colored QDs by controlling the emission wavelength via the microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis. To further show the performance of the QDs, CuInZnS/ZnS QDs have been successfully employed for HeLa cancer cell imaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...