Insight into the Claisen condensation of methyl acetate and dimethyl carbonate to dimethyl malonate†
Abstract
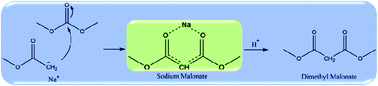
A mechanistic study on the synthesis of dimethyl malonate (DMM) via condensation of methyl acetate (MA) and dimethyl carbonate (DMC), catalyzed by sodium methoxide, has been conducted using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and density functional theory calculations. The results indicated that the Claisen condensation of MA and DMC in the presence of methoxide yielded (CH3OCO)2CHNa (DMNa) instead of DMM since DMM is easily deprotonated by the methoxide catalyst. Further protonation after the condensation by adding a proton-donor reagent is essential to obtain DMM. Based on the experimental results, a detailed reaction mechanism for the condensation of MA and DMC into DMM in the presence of methoxide has been proposed and disclosed by computational calculations. Besides, it has been proven that the base strength of the catalyst has a critical effect on the condensation reaction and the DMM yield.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...