Synthesis of K–Pd doped NiCo2O4−δ by reactive calcination route for oxidation of CO–CH4 emissions from CNG vehicles
Abstract
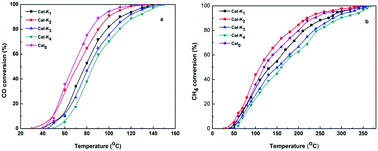
The present study is devoted to formulating a doped spinel catalyst by a novel route of calcination for the oxidation of the CO–CH4 mixture emitted from compressed natural gas (CNG) vehicles. The K, Pd and K–Pd doped NiCo2O4 catalysts were prepared by co-precipitation of basic carbonates of Ni and Co followed by doping of the promoters and reactive calcination in 4.5% CO–air environment. The catalysts were characterized by XRD, TPR, BET SEM-EDX and XPS. The activity test of the catalysts were performed in a fixed-bed-tubular-reactor under the following conditions: 500 mg catalyst, 1.5% CO, 1.5% CH4, 97% air, 100 mL min−1 total gas flow-rate at atmospheric pressure. The optimized composition of dopants in the catalyst for the oxidation reaction was 2 wt% K and 0.1 wt% Pd. The catalysts were highly selective for CO2 formation as no other byproduct was detected in the reaction under the conditions studied. The characterization revealed that the dopants in the catalysts improved the catalyst reducibility and changed its redox properties, increased the surface area, and also created oxygen deficiencies in the spinel structure. The performance of the 2%K0.1%Pd–NiCo2O4 catalyst was the best, with the total oxidation of CO–CH4 mixture at ∼320 °C. The temperature for complete combustion of the CO–CH4 over 2%K–NiCo2O4 (342 °C) was in between the 0.1%Pd-doped (335 °C) and undoped (350 °C) catalysts. The activity order of the catalysts was as follows: K–Pd–NiCo2O4 > Pd–NiCo2O4 > K–NiCo2O4> NiCo2O4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...