Inner versus outer sphere metal-monoamide complexation: ramifications for tetravalent & hexavalent actinide selectivity†
Abstract
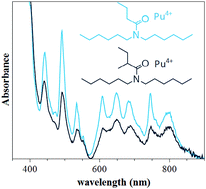
Oxidation of americium to the hexavalent state could streamline used nuclear fuel management through a group hexavalent actinide separation process. Monoamides, N,N-dialkyl amides, are being considered in this work due to their selectivity towards hexavalent, over tetravalent, actinides. Hexavalent selectivity arises when the monoamides contain a branched acyl chain. While this selectivity has been known since preliminary studies by Siddall, structures of the extracted species have only recently been investigated. This study expands on other research efforts by examining the structure–extraction functionality of straight and branched monoamides with Pu4+ and PuO22+. In both Pu oxidations states, the effect of acyl chain length was investigated by comparing Pu extraction and UV-vis spectra of Pu complexes with N,N-dihexylbutyramide, N,N-dihexylvaleramide, and N,N-dihexylhexanamide. Furthermore, the effects of alkyl chain branching were investigated by comparing N,N-dihexyl(2-methyl)butyramide and N,N-dihexyl(2-methyl)valeramide, as well as ethyl branched N,N-dihexyl(2-ethyl)butyramide and N,N-dihexyl(2-ethyl)hexanamide. These structure–extraction relationships were characterized by collecting UV-vis spectra of the metal-monoamide extracted species and tracer distribution studies. The UV-vis analysis was found to match distribution values collected under radiotracer conditions and indicated Pu was extracted as the tetra- and hexanitrato monoamide complex for Pu4+ and the bis- or trisnitrato species for PuO22+. The monoamides’ ability to recover Cu3+ periodate oxidized Am was also studied using radiotracer methods. Initial efforts with nitric acid pretreated monoamides, salting agents, and synergistic studies with di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (HDEHP) were ineffective. Pretreatment with sodium bismuthate was found to improve Am recovery, and distributions above one were achieved with straight chain monoamides at 3 M HNO3.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...