An overview of recent progress in solvent systems, additives and modifiers of counter current chromatography
Abstract
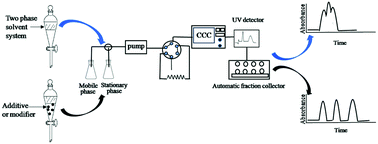
The chromatographic selectivity of counter current chromatography is highly dependent on the partition coefficient (K) values of solutes. Therefore, the successful separation of counter current chromatography necessitates an appropriate biphasic solvent system which provides an ideal range of K values. In fact, combinations of solvents that produce biphasic solvent systems are almost limitless. It is possible to use two, three or more solvents, which means that it is possible to adjust the selectivity by addition of a solvent that has some affinity towards the two phases of a biphasic system. In addition, many researchers have found that the separation efficiency of counter current chromatography can be improved by adding additives or modifiers into the solvent system. This overview is mainly focused on the development of solvent systems, additives and modifiers including traditional two-phase solvent systems, three phase solvent systems, aqueous two-phase solvent systems, chiral selectors, ionic liquid modifiers, ion-pair forming additives, metal ions, anionic surface active agents, pH modifiers and other additives.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...