Effect of geometry factors on the priority of σ-hole⋯π and π-hole⋯π bond in phosphorescent cocrystals formed by pyrene or phenanthrene and trihaloperfluorobenzenes†
Abstract
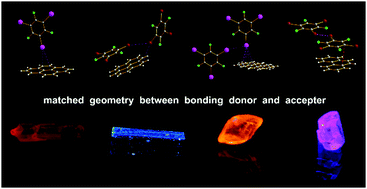
Introducing heavy atom perturbers such as iodine and bromine with σ-hole⋯π or π-hole⋯π bonds into cocrystals is an effective way to induce phosphorescence in the design of new luminescent materials containing rigid and planar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with large conjugated π-electron systems. The bonding donors usually used such as halo- or multihaloperfluorobenzenes possess both a σ-hole and a π-hole. One question is under what condition do σ-hole or π-hole bonding, or both, occur? It is proposed that in some cases the geometry of the bonding donors should be one of the key factors, besides the difference of molecular surface electrostatic potential (SEP) of the σ-hole and π-hole, and the interaction energy, in influencing bonding patterns in cocrystals. That is, a thicker multi-haloperfluorobenzene ring (caused by a larger halogen atom radius) is not beneficial to π-hole⋯π bonding. However, a multi-haloperfluorobenzene, due to its larger size, can reach the vertically adjacent π-system in a π-hole⋯π bonding pair to produce a typical above-plane σ-hole⋯π bond, or directly produce a σ-hole⋯π bond without a π-hole⋯π bond, as the SEP of a σ-hole is 65 kJ mol−1 higher than a π-hole. Therefore, four cocrystals of Pyr-TIPB (1), Pyr-TBrPB (2), Phe-TIPB (3) and Phe-TBrPB (4) were prepared. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, computation of SEP and interaction energy reveal that the very typical σ-hole⋯π bonding in Pyr-TIPB (1) and Phe-TIPB (3) has priority over π-hole⋯π bonding and other interactions because of the larger size and thicker TIPB, while π-hole⋯π bonding in Pyr-TBrPB (2) and Phe-TBrPB (4) has priority over σ-hole⋯π bonding and other interactions because of the smaller and thinner TBrPB. Moreover, red phosphorescence of pyrene in cocrystalline Pyr-TIPB assembled by halogen bonding was observed for the first time under UV-365 at room temperature because of the typical above-plane C–I⋯π bond.
- This article is part of the themed collections: 1st International Conference on Noncovalent Interactions and The halogen bond: a new avenue in recognition and self-assembly


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...