A low affinity nanoparticle based fluorescent ratiometric probe for the determination of Zn(ii) concentrations in living cells†
Abstract
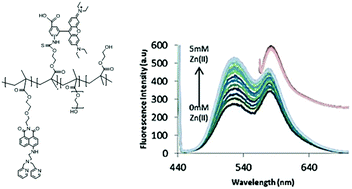
A ratiometric polymeric fluorescent probe for Zn(II) was developed comprising a Zn(II) responsive naphthalimide sensing unit and a Zn(II) insensitive rhodamine based calibration fluorophore attached to a common poly(methyl methacrylate) backbone. The Zn(II) responsive unit was designed to operate according to the photoinduced electron transfer (PET) mechanism with the naphthalimide fluorescence intensity increasing with increasing Zn(II) concentration. The amphiphilic polymeric probe was found to self-assemble in aqueous solution to generate nanoparticles with a hydrodynamic diameter of 10.61 ± 7.61 nm. Good selectivity for Zn(II) was observed when tested against a range of physiological relevant cations and excellent linearity (R2 = 0.99) was demonstrated in the 0–5.0 mM Zn(II) range when the ratiometric intensity (I527/I580) was plotted as a function of Zn(II) concentration. The probe was also capable of discriminating between resting and high Zn(II) levels in living cells using confocal fluorescence microscopy and exhibited no evidence of cellular toxicity. Combined, these results highlight the potential of the nanoparticle probe as a low-affinity ratiometric sensor for Zn(II) compatible with use in living cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...