Fabrication of a 2,4-dinitrophenol sensor based on Fe3O4@Ag@Ni nanomaterials and studies on their antibacterial properties†
Abstract
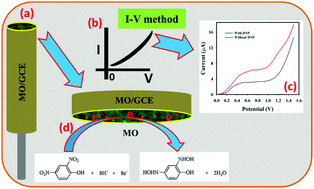
Fe3O4@Ag@Ni nanoparticles (MO) were synthesized and characterized. In this study, a reduction method was utilized to synthesize the nanoparticles. The Fe3O4@Ag@Ni nanoparticles were cubic with an about 15 nm particle size, established by both TEM and XRD. EDS mapping provided information about the distribution of the materials in the matrix. Optical properties were observed through photoluminescence (PL) studies. Electrochemical sensor applications of Fe3O4@Ag@Ni were assessed. A thin layer of Fe3O4@Ag@Ni nanomaterial film as a chemical sensor was fabricated on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) with a 5% nafion conducting binder. The sensor was successfully applied for the detection of 2,4-dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP) using a reliable I–V method at low potential. The sensor-attributes including good sensitivity (3.5217 μA μM−1 cm−2), low detection limit (5.4 ± 0.1 pM; at a signal to noise ratio of 3), low limit of quantification (18.0 ± 0.1 pM), good reliability, good reproducibility, ease of integration, and long-term stability were explored. The sensor response towards 2,4-DNP is linear over a large concentration range (0.1 nM to 1.0 mM). This work initiated a route for sensitive sensor development based on MO nanomaterials using a reliable I–V approach for the detection of hazardous and carcinogenic toxins in environmental and health care fields. The Fe3O4@Ag@Ni nanomaterial showed anti-microbial activity as appraised by a zone of inhibition parameter study, which showed a positive test both for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The highest inhibition zone to well diameter ratio was 3.5, higher than imipenem (ipm 10).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...