Synthesis and properties of five ring fused aromatic compounds based on S,S-dioxide benzothiophene†
Abstract
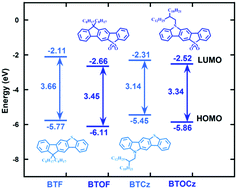
Asymmetrical five ring fused compounds based on S,S-dioxide benzothiophene, 9,9-dioctylfluorene[2,3-b]benzo[d]thiophene-S,S-dioxide(BTOF) and N-(2-decyltetradecyl)carbazole[2,3-b]benzo[d]thiophene-S,S-dioxide (BTOCz) were synthesized and characterized. BTOF and BTOCz were readily soluble in common organic solvents and exhibited high thermal stability with the melting points (Tms) of 119 °C and 150 °C, and thermal decomposition temperatures (Tds) of 280 °C and 338 °C, respectively. The highest occupied molecular orbital energy levels (HOMOs), the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy levels (LUMOs) and the band gaps (Egs) of BTOF and BTOCz were −6.11, −2.66 and 3.45 eV, −5.86, −2.52 and 3.34 eV, respectively. The photoluminescence (PL) spectra of BTOF and BTOCz were peaked at 404 and 420 nm in film, and the photoluminescence quantum yields (QPLs) were 30% and 10% in toluene solution, respectively. BTOF and BTOCz showed strong intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) character, relatively high QPLs and deeper HOMO and LUMO levels compared with compounds BTF and BTCz. Compared with the symmetrical seven ring fused compounds FBTO and CzBTO, the asymmetrical five ring fused compounds BTOF and BTOCz showed relatively shallow HOMO levels, which can facilitate hole injection, and therefore, could be potential construction units in organic semiconductors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...