Synthesis of a bimetallic conducting nano-hybrid composite of Au–Pt@PEDOT exhibiting fluorescence†
Abstract
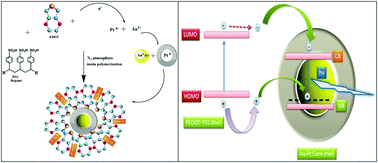
Inorganic–organic conducting nano hybrids are the new class of materials. Au–Pt@PEDOT was further explored due to its attractive features such as ultrafine size, low toxicity and fluorescent properties in the blue region of the visible spectrum. In the present study Au–Pt@PEDOT with photoluminescence (PL) quantum efficiency of 51% was synthesized in situ in one step in water via an unpretentious blending technique. The formation of core–shell nanocomposite was evidently supported with transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and FT-IR spectroscopy. The hole–electron transport mechanism within the nanocomposite was systematically investigated with PL spectroscopy, time resolved florescence spectroscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and cyclic voltammetry. The average PL life time decay of a nanocomposite was found to be 2.75 ns. The conducting shell of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) through its π–π interactions provides effective shielding to the core shell nanoparticles. As a result, the intra-molecular vibrations and rotation are greatly suppressed, which reduce the non-radiative relaxation of excited states, thus predominantly increasing the photoluminescence quantum efficiency and decrease the PL life time decay of the nano-composite.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...