A green approach for synthesizing silver nanoparticles, and their antibacterial and cytotoxic activities†
Abstract
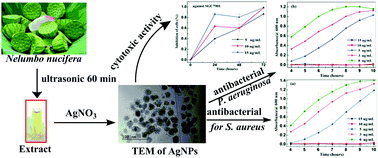
Lotus has been widely used as the economic staple vegetable for the preparation of soups and braised dishes in China. Its extracts have been employed as functional foods for their diuretic, astringent, fever-reducing and heat-clearing effects, and to treat hemostasis and obesity. We present herein a new eco-friendly approach for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by using the lotus aqueous extract as a reducing and stabilizing agent. The AgNPs so-prepared were quasi-spherical in shape and uniformly dispersed, with an average diameter of 12.9 ± 3.7 nm. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) revealed that water soluble biomolecules from the lotus extract played important roles in the formation of the AgNPs. The AgNPs displayed distinctive antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. The results confirmed that the lotus can be a low-cost, nontoxic and eco-friendly natural resource for the synthesis of AgNPs, which might be useful for the development of new alternative antibacterial and anticancer agents in biomedicine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...