Enhanced visible light driven photocatalytic activity of CdO–graphene oxide heterostructures for the degradation of organic pollutants
Abstract
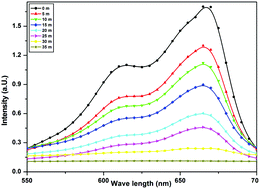
Synthesis of efficient CdO based photocatalysts for enhanced visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants mostly emphasize on (1) increase of surface area of the photocatalyst and (2) high charge separation and suppressed recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. CdO/GO nanocomposites with different weight ratios of GO synthesized by in situ deposition of CdO nanoparticles on graphene oxide sheets via a solution phase approach without the use of any templates or surfactants could provide a larger surface area for photocatalytic degradation and enhanced charge separation due to electronic interactions between CdO and GO. The efficiency of CdO/GO materials for degradation of organic pollutants was investigated against methylene blue (MB), methyl orange (MO) and rhodamine-B (RhB) dyes as test pollutants. The results showed a much higher photocatalytic activity of CdO/GO nanocomposites than that of pure CdO nanoparticles under visible light irradiation and the nanocomposite having 3.3% GO (CG-2) possessed the highest photocatalytic activity. The enhanced photocatalytic activity of CdO/GO nanocomposites could be assigned to the increased adsorbability of dye molecules, high charge separation and suppressed recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs, all of which result from the introduction of GO. These results revealed the great potential of such graphene-based semiconductor nanocomposites as visible-light photocatalysts for water remediation applications in future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...