Development of self-repair nano-rod scaffold materials for implantation of osteosarcoma affected bone tissue†
Abstract
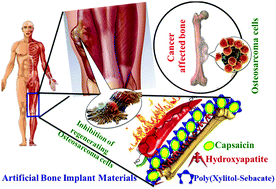
Osteosarcoma is the most widely recognized fatal bone disease in children and young adults. The osteosarcoma affected places of bone implant materials lose their activity after a period of time due to the possibility of regenerating sarcoma cells. Hence, the complete recovery of this disease is very challenging. Subsequently, new helpful methodologies, including natural antioxidant loaded bone implant materials, are effectively used to treat osteosarcoma cells. In this regard, nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced with a xylitol based poly(xylitol sebacate) PXS co-polymer together with a capsaicin loaded scaffold was investigated on osteosarcoma cells. The physicochemical properties of the scaffold were evaluated by FT-IR (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy), SEM (scanning electron microscopy), TEM (transmission electron microscopy), and XRD (X-ray diffraction). The in vitro release and antioxidant activity of the capsaicin loaded nHAP/PXS/CAP scaffold were evaluated by UV-Visible spectroscopy. Cytotoxicity against the Saos-2 cancer line and cell viability in the osteoblast cell MG63 are reported. Eventually, the composite enlarges the creation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Saos-2 cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...