The excellent dye-photosensitized degradation performance over hierarchical BiOCl nanostructures fabricated via a facile microwave-hydrothermal process
Abstract
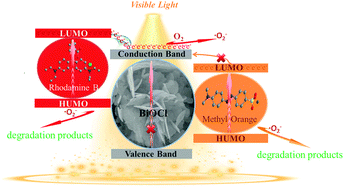
Via a facile microwave-hydrothermal process, a series of BiOCl crystals with different morphologies was synthesized using hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride (HTAC) as the chlorine source and structure directing agent by precisely controlling the synthesizing temperatures (100–180 °C). The results show that a high temperature is favorable for the formation of 2D disk-like BiOCl nanosheets and a low temperature benefits the formation of 3D porous flower-ball-like BiOCl aggregations. At the same time, the thickness of the 2D nanosheet building units in 3D hierarchical BiOCl flowers gradually decreased with a decrease of temperature. Compared to disk-like BiOCl, the 3D hierarchical BiOCl structures have distinct advantages, e.g. a large surface area and rich porous structure, which allows their strong adsorption for reaction substrate molecules. Moreover, the photoelectrochemical test results further revealed that 3D hierarchical BiOCl crystals possess much smaller electron transfer impedance and larger photocurrent response values than disk-like BiOCl units due to the continuous and intense electron injection from excited Rhodamine B, which is favorable for the continuous generation of superoxide radicals (˙O2−). Thus, BiOCl with a 3D hierarchical structure exhibited a superior dye-sensitized degradation activity for single Rhodamine B and mixed dyes (Rhodamine B and methyl orange) under visible light illumination. These results are expected to provide new insights for the rapid fabrication of 3D hierarchical BiOX materials without using any organic solvent. Moreover, the mechanism for the effect of the microstructure of BiOCl on the dye-photosensitized reaction process was illuminated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...