Systematic mutagenesis of oncocin reveals enhanced activity and insights into the mechanisms of antimicrobial activity†
Abstract
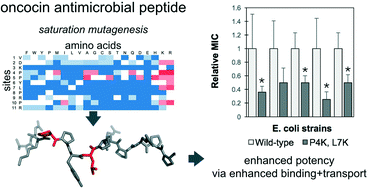
Oncocin is a proline-rich antimicrobial peptide that inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial ribosome. In this work, the antimicrobial activity of oncocin was improved by systematic peptide mutagenesis and activity evaluation. We found that a pair of cationic substitutions (P4K and L7K/R) improves the activity by 2–4 fold (p < 0.05) against multiple Gram-negative bacteria. An in vitro transcription/translation assay indicated that the increased activity was not because of stronger ribosome binding. Rather a cellular internalization assay revealed a higher internalization rate for the optimized analogs thereby suggesting a mechanism to increase potency. In addition, we found that the optimized peptides' benefit is dependent upon nutrient-depleted media conditions. The molecular design and characterization strategies have broad potential for development of antimicrobial peptides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...