Synthesis and potential antineoplastic activity of dehydroabietylamine imidazole derivatives†
Abstract
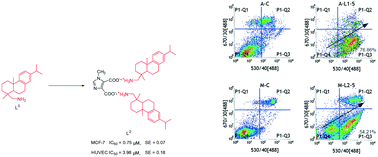
To seek more efficient and lower toxicity anticancer compounds, several imidazole combining dehydroabietylamine derivatives including organic salts (L1–L2) and amides (L3–L5) were synthesized. Their antineoplastic activity against HeLa (cervix), MCF-7 (breast), A549 (lung) and HepG2 (liver) cells and HUVECs (umbilical vein, normal cells) in vitro were evaluated by MTT assay. The results unequivocally showed that nearly all compounds had better antineoplastic activity and lower toxicity than dehydroabietylamine (L0). For MCF-7 cells, L2 (0.75 μM) and L5 (2.17 μM) had higher anti-MCF-7 activity than L0 and DOX. For A549 cells, L1 (1.85 μM) and L2 (4.37 μM) had higher anti-A549 activity than L0; in particular, the IC50 value of L1 was much lower than that of DOX. Among these investigated compounds, L2 and L5 had lower IC50 values (0.75 μM and 2.17 μM) against MCF-7 cells and lower toxicity, which suggested that they may be potential future anticancer drugs. In addition, L1 and L2 could suppress cancer cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis. L1–L5 could bind with DNA through intercalation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...