Design, synthesis and antimicrobial activity of usnic acid derivatives
Abstract
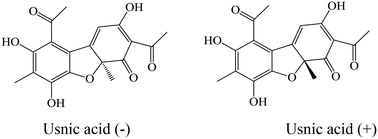
Usnic acid, a dibenzofuran, was originally isolated from lichens producing secondary metabolites, and is well known as an antibiotic, but is also endowed with several other interesting properties. Thus, the goal of this paper is the design of new usnic acid derivatives and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. All newly synthesized compounds possess good antibacterial activity with MIC ranging from 1.02–50.93 × 10−2 mmol mL−1 and MBC from 2.05–70.57 × 10−2 mmol mL−1. The most sensitive bacterial species was Staphylococcus aureus, while Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli were the most resistant among the ATCC strains, and MRSA was the most resistant among all tested bacteria (ATCC and clinical isolates). Their antifungal activity was very strong (MIC = 0.35–7.53 × 10−2 mmol mL−1 and MFC = 0.70–15.05 × 10−2 mmol mL−1) – better than those of reference compounds and usnic acid itself. The most sensitive fungal species was Trichoderma viride, while Penicillium versicolor var. cyclopium appeared to be the most resistant. It should be mentioned that in general most of the compounds showed weaker antibacterial activity, but better antifungal properties than usnic acid itself. The results allow us to conclude that the title compounds are good lead compounds for novel more active antibacterial drugs. On the other hand, these compounds are very promising as antifungals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...