Allenamide as a bioisostere of acrylamide in the design and synthesis of targeted covalent inhibitors†
Abstract
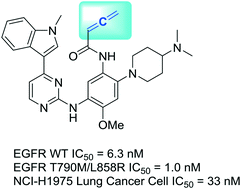
The success of acrylamide-containing drugs in treating cancers has spurred a passion to search for acrylamide bioisosteres. In our endeavour, we have identified that an allenamide group can be a reactive bioisostere of the acrylamide group. In our development of allenamide-containing compounds, we found that the most potent compound, 14, inhibited the kinase activities of both T790M/L858R double mutant and wild type EGFR in a low nM range. 14 also inhibited the growth of NCI-H1975 lung cancer cells at IC50 = 33 nM, which is comparable to that of acrylamide-containing osimertinib. The western blot analysis showed that the phosphorylation of EGFR, AKT, and ERK1/2 was simultaneously inhibited in a dose-dependent manner when NCI-H1975 cells were treated with 14. By measuring the conjugate addition product formed by 14 and GSH, we obtained a reaction rate constant of 302.5 × 10−3 min−1, which is about 30-fold higher than that of osimertinib. Taken together, our data suggest that the allenamide-containing compounds inhibited EGFR kinases through covalent modifications. Our study indicates that the allenamide group could serve as an alternative electrophilic warhead in the design of targeted covalent inhibitors, and this bioisostere replacement may have broad applications in medicinal chemistry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...