Charge-controlled microfluidic formation of lipid-based single- and multicompartment systems†
Abstract
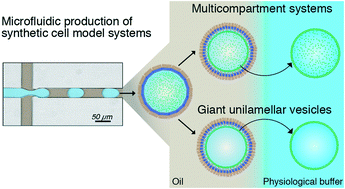
In this manuscript, we introduce a simple, off-the-shelf approach for the on-demand creation of giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) or multicompartment synthetic cell model systems in a high-throughput manner. To achieve this, we use microfluidics to encapsulate small unilamellar vesicles in block-copolymer surfactant-stabilized water-in-oil droplets. By tuning the charge of the inner droplet interface, adsorption of lipids can be either inhibited, leading to multicompartment systems, or induced, leading to the formation of droplet-stabilized GUVs. To control the charge density, we formed droplets using different molar ratios of an uncharged PEG-based fluorosurfactant and a negatively-charged PFPE carboxylic acid fluorosurfactant (Krytox). We systematically studied the transition from a multicompartment system to 3D-supported lipid bilayers as a function of lipid charge and Krytox concentration using confocal fluorescence microscopy, cryo-scanning electron microscopy and interfacial tension measurements. Moreover, we demonstrate a simple method to release GUVs from the surfactant shell and the oil phase into a physiological buffer – providing a remarkably high-yield approach for GUV formation. This widely applicable microfluidics-based technology will increase the scope of GUVs as adaptable cell-like compartments in bottom-up synthetic biology applications and beyond.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...