Sample temperature effect on laser ablation and analytical capabilities of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy
Abstract
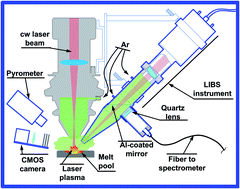
The influence of sample temperature on the laser ablation process and analytical capabilities of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) was studied systematically. We were interested in estimating the analytical capabilities of a LIBS probe which was developed for in situ elemental analysis of molten metals during the production of metal parts by additive manufacturing. The sample surface was heated locally (4 mm diameter spot) in an argon atmosphere using a powerful continuous wave fiber laser while a nanosecond laser ablated only a small spot (0.3 mm diameter) in the high temperature area. This procedure can be utilized for high temperature LIBS studies of any samples including materials with high melting temperatures (tungsten, aluminum oxide etc.). Low alloy steel samples were heated up to their melting points and LIBS experiments were carried out in a wide temperature range (25–1600 °C). LIBS plasma imaging revealed that the size and brightness of the expanding plume did not depend on solid sample temperature but these parameters increased manifold for molten steel ablation. Comparison of plasma emissivity, temperature and electron density did not reveal any meaningful differences in the case of LIBS measurements for room temperature (25 °C), hot solid (1050 °C) and molten (1550 °C) targets, and thus enhanced plasma emissivity was attributed to greater ablation rate. The surface temperature impact on LIBS analytical capabilities was studied by comparing calibration curve linearity, limits of detection and the root mean square error of cross-validation for chromium, silicon and manganese. High temperature of the sample surface favored greater atomic/ionic line emission but molten sample LIBS analysis revealed poor limits of detection for all elements, which was explained by strong fluctuations of the laser ablation process at the liquid metal surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...