Lead isotopic analysis of Antarctic snow by quadrupole ICP-MS using a total-consumption sample introduction system
Abstract
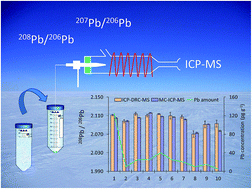
Measurement of lead isotope ratios in snow samples using inductively coupled plasma-dynamic reaction cell-mass spectrometry (ICP-DRC-MS) at a low sample consumption rate was thoroughly studied. Sample volumes were reduced from 20.0 to 0.200 mL by freeze-drying, and the pre-concentrates were efficiently introduced into the plasma source at 20 μL min−1 by using the heated torch-integrated sample introduction system (hTISIS). In addition, the DRC was pressurised with neon to improve the precision by collisional damping. Sensitivity was maximised by optimising the operating parameters of the sample introduction system (nebulizer/sheathing gas flow rate ratio), the reaction cell (rod offset and damping gas flow rate) and the signal measurement conditions. The developed method was then characterised in terms of the analytical working range, accuracy and uncertainty estimation. Under the optimal conditions, isotope ratios did not differ in the 0.1–20 μg L−1 range. Internal precision, expressed as relative standard deviation, varied from 0.12 to 0.18% (c = 10 μg L−1; n = 12), while the external precision was <0.1%. The potential influence of the pre-concentration procedure on the analytical data was carefully investigated in terms of blank contribution, recovery and isotopic fractionation. The lowest Pb concentration needed in the samples to limit the influence of the blanks within an experimental precision of 0.5% was 4.4 pg g−1, and the recovery of five standard reference solutions with a Pb concentration of 100 ng L−1 was 90 ± 5%, with no significant isotopic fractionation. The developed ICP-DRC-MS method was finally applied to a number of representative Antarctic snow samples previously characterised by multi-collector ICP-MS, obtaining a satisfactory agreement between the data provided by the two techniques and analytical results consistent with literature data on the glaciochemistry of Antarctic ice cores.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...