Renewable protein-based monomer for thermosets: a case study on phthalonitrile resin†
Abstract
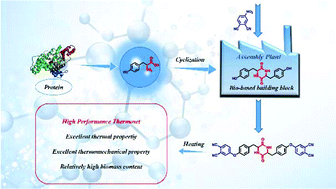
Further enriching the source of bio-based raw materials for thermosets is of significant importance in the current development context. In this paper, we synthesized a novel bio-based phthalonitrile monomer derived from L-tyrosine to verify the feasibility of a bio-based L-tyrosine molecular design platform for thermosets, and to prove that the L-tyrosine building-block can confer high performance. The biomass content of L-tyrosine-based phthalonitrile monomer reaches 56%, higher than other bio-based phthalonitrile resins. The structure was confirmed by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) and elemental analyses. The curing behavior was investigated by FTIR spectra, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and in situ FTIR spectra. The processability was studied by rheological analysis. And a study of the curing kinetics of the TPN monomer was carried out by non-isothermal DSC. Finally, the physical properties of the cured polymer were evaluated by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The results indicate that the phthalonitrile resin exhibited a high glass transition temperature (Tg) and excellent thermal properties compared with petroleum-based bisphenol A phthalonitrile resin. The results also demonstrate that introducing L-tyrosine into thermosets is feasible and can simultaneously impart excellent performances to the materials with relatively high level of biomass.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...