Macroporous–mesoporous carbon supported Ni catalysts for the conversion of cellulose to polyols†
Abstract
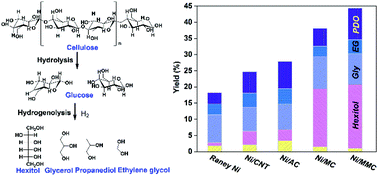
Carbon based materials are some of the most commonly studied catalysts for the conversion of cellulose to polyols. The catalytic performance of these materials, however, is typically limited by the access of the substrate to the active sites, which is governed by the poor solubility of cellulose in aqueous solutions. In an attempt to resolve this, we presented a novel hierarchical carbon material which was synthesized by a dual-templating method. Transmission electron microscopy and porosity measurements confirmed that the resultant materials consisted of both spherical macropores and well-defined mesoporous channels. Additional characterisation of this material revealed that it has an exceptionally high surface area (>1110 m2 g−1) and a high concentration of acidic sites, which are considered to be crucial for the hydrolysis of cellulose. Ni nanoparticles were subsequently immobilised onto this material and some additional carbon supports. It was determined that the high surface area and porosity of the synthesised carbon material assisted with the dispersion of the Ni nanoparticles. This Ni catalyst was found to be highly efficient for the one-pot conversion of cellulose to polyols, which is proposed to be a consequence of both the high number of acid sites and excellent Ni dispersion. This approach to catalyst design, offers a novel method for the valorisation of cellulose.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...