In situ MnOx/N-doped carbon aerogels from cellulose as monolithic and highly efficient catalysts for the upgrading of bioderived aldehydes†
Abstract
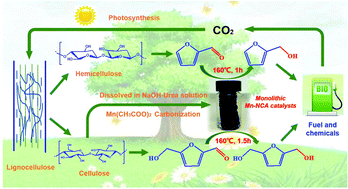
Herein, we report a sustainable route to in situ synthesize a monolithic MnOx/N-doped carbon aerogel catalyst (Mn-NCA) by pyrolysing MnO(OH)2-cellulose aerogel precursors based on an alkali–urea aqueous system. The as-obtained Mn-NCA showed highly efficient catalytic activity for the transfer hydrogenation of a broad range of biomass-derived aldehydes, yielding 90–100% conversion and 64–100% selectivity to the corresponding alcohols under mild conditions in an oven without agitation. A combination of controlled experiments and detailed characterization studies indicated that the superior performance of Mn-NCA is attributed to the monolithic three-dimensional (3D) hierarchical porous architecture and the synergistic effects between homogeneously dispersed MnOx nanoparticles (NPs) and urea-derived basic sites. The monolithic feature of Mn-NCA exhibits superior dispersibility and separability compared to conventional centrifugation and filtration techniques in a powdery catalytic system. Moreover, a possible reaction mechanism is proposed. Our work provides a new method for developing highly efficient monolithic catalysts from renewable biopolymers for biomass valorization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...