The effect of different Brønsted acids on the hydrothermal conversion of fructose to HMF†
Abstract
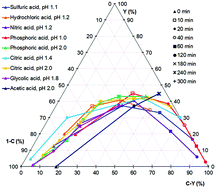
The hydrothermal dehydration of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), a promising platform chemical from renewable resources, is commonly known to be Brønsted acid catalysed. However, it is not clear whether the acids used as catalysts may have an additional effect on the reaction, besides the donation of protons. In this work, we studied the effect of different Brønsted acids on the hydrothermal conversion of fructose to HMF. In particular, phosphoric acid, if present in a high concentration, leads to a significantly stronger acceleration of the reaction than would be expected from the pH value, calculated under hydrothermal conditions. Acetic acid, on the other hand, seems to evoke an alternative reaction mechanism. The maximal HMF yield however is essentially unaffected by the pH value or the type of acid used.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...