Unprecedented catalytic performance in amine syntheses via Pd/g-C3N4 catalyst-assisted transfer hydrogenation†
Abstract
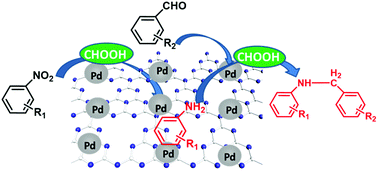
The preparation of amine compounds is very important for both the chemical industry and renewable feedstock processing. Nevertheless, difficulties remain in finding a catalytic system that is sufficiently active and environmentally benign for producing amine compounds. In this work, we report that g-C3N4 nanosheets as support materials can significantly boost the efficiency of Pd nanoparticles for the reduction of nitro compounds to primary amines. Using formic acid as a hydrogen donor and water as a solvent, the optimized 5 wt% Pd/g-C3N4 catalyst exhibited an unprecedented performance in the conversion of nitrobenzene into aniline (achieving almost full conversion with an extremely high turnover frequency of 4770 h−1 at room temperature), yielding the best activity ever reported for heterogeneously catalyzing nitro compound reduction. Pd/g-C3N4 catalyst was also active for the one-pot reductive amination of carbonyl compounds with nitro compounds to obtain the corresponding secondary amines with excellent selectivity (>90%). We proposed that the protic N–H+ and hydridic Pd–H− on Pd/g-C3N4 are the active species for the transfer hydrogenation reaction of nitro compounds. Furthermore, Pd/g-C3N4 catalyst was highly stable with a wide scope in the syntheses of various amine compounds. This work will open up a new approach for the transfer hydrogenations of nitro compounds to produce primary or secondary amines in green chemistry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...