Biosourced analogs of elastomer-containing bitumen through hydrothermal liquefaction of Spirulina sp. microalgae residues†
Abstract
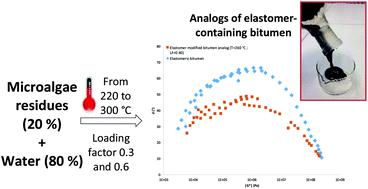
The hydrothermal liquefaction of Spirulina sp. microalgae (i.e. cyanobacteria) byproducts was investigated for the production of road binders from renewable sources. In the 220–300 °C temperature range, a water-insoluble viscous material was obtained in a ca. 50% yield, which consisted of an oily fatty acid-based fraction mixed with organic and inorganic solid residues (ca. 20%). More interestingly, this material exhibited viscoelastic properties similar to elastomer-containing bitumen, when operating the hydrothermal liquefaction between 240 and 260 °C. This is the first example of a bio-sourced product showing such properties. At higher temperature, fragmentation of species of high molecular weight occurred, resulting in less viscous materials that were no more thermorheologically simple. The reactor filling ratio was also allowed to vary (i.e. 30% versus 60%), showing very little influence in terms of yield and viscoelastic properties of the resulting bio-binders.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...