Blueberry extract promotes longevity and stress tolerance via DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans†
Abstract
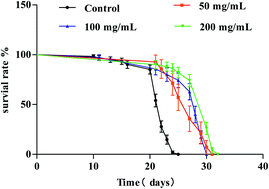
Blueberry is rich in bioactive phytochemicals with a wide of range of biological activities and health benefits. However, little is known about their effects on aging. The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effects of supplementation with a blueberry extract (BE) on lifespan and stress resistance using Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) as a model. The mechanisms of these effects were explored using RNAi technology. The mean lifespan of C. elegans treated with BE at 50, 100, and 200 mg mL−1 was significantly increased by 22.2%, 36.5%, and 44.4%, respectively, in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, supplementation with BE improved motility and decreased lipofuscin accumulation. C. elegans pretreated with BE were more resistant than untreated C. elegans to stresses (heat, ultraviolet-B radiation, and paraquat). Treatment with BE resulted in up-regulation of genes related to antioxidant systems, including sod-3, cat-1, mev-1, skn-1, mek-1, nhr-8, and daf-16. Suppression of daf-16 by RNAi shortened the lifespan of C. elegans and inhibited the expression of sod-3, suggesting that BE may regulate sod-3 downstream of daf-16 to extend lifespan and stress resistance. Our findings revealed that, in C. elegans, BE can prolong the lifespan, improve health indexes, and enhance stress resistance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...