Preventive mechanism of bioactive dietary foods on obesity-related inflammation and diseases
Abstract
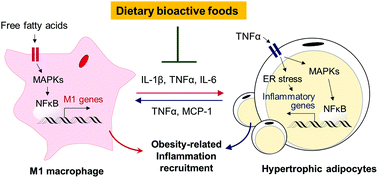
Obesity is associated with low-grade chronic inflammation of adipose tissue, which leads to the development of metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and cancer. Obesity and a high calorie diet are associated with altered endocrine and metabolic functions of adipose tissue, contributing to systemic inflammation as a result of the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines/adipokines into the circulation and metabolic endotoxemia. Furthermore, the accumulation of proinflammatory macrophages within the visceral adipose tissue may also be a major cause of chronic inflammation of adipocytes. Thus, it is important to understand the factors that regulate the function of both adipocytes and macrophages to find attractive strategies against the burden of obesity-induced health problems. Although the vast range of activities of dietary bioactive compounds on obesity and inflammation have been widely investigated, the mechanisms underlying their beneficial effects on obesity-associated inflammatory response are still poorly understood. This review focuses on the molecular biology mechanism of obesity-induced inflammation and the reciprocal interactions between the major molecular mechanisms and a range of dietary bioactive compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...