Protective effects of sesamol on systemic oxidative stress-induced cognitive impairments via regulation of Nrf2/Keap1 pathway†
Abstract
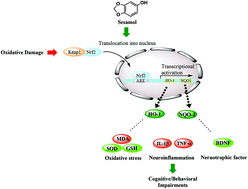
Oxidative stress is considered as a pivotal culprit in neurodegenerative diseases and brain aging. The aim of present study was to investigate antioxidative and neuroprotective effects of sesamol, a phenolic lignan from sesame oil, on oxidative stress induced neuron damage and memory impairments. C57BL/6J mice were treated by intraperitoneal injections of D-galactose for 8 weeks. Sesamol treatment (0.05% w/v, in drinking water) suppressed D-galactose-induced liver damages and improved HO-1 and NQO1 mRNA levels. Behavioral tests, including Y-maze test and water maze-test, revealed that sesamol significantly improved oxidative stress-induced cognitive impairments. Meanwhile, sesamol ameliorated neuronal damage and improved BDNF level in rat hippocampus. Sesamol elevated mRNA levels and protein expressions of antioxidant enzymes HO-1 and NQO1 as well as decreased inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β in D-galactose-treated mice serum. In addition, activity of CAT and GSH level were increased in sesamol-treated mice serum. Moreover, sesamol treatment also balanced cellular redox status, protected mitochondrial dysfunction and upregulated antioxidant enzymes by activating the Nrf2 transcriptional pathway and its nuclear translocation in H2O2-treated SH-SY5Y cells. In conclusion, these results revealed that sesamol could be a potential neuroprotective agent during aging process due to its beneficial effects on liver–brain axis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...