Molecular mechanisms of the anti-obesity effect of bioactive ingredients in common spices: a review
Abstract
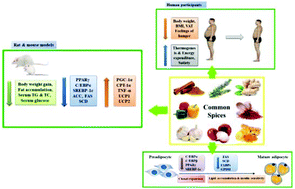
Obesity is a health concern related to many metabolic disorders. In the prevention and treatment of overweight, medicines and bariatric surgeries are major strategies but there are side effects. A variety of naturally occurring bioactive ingredients derived from common spices, including cinnamon, rosemary, ginger, pepper, saffron, garlic, onion and turmeric, have been proved to have weight-loss effects. In this work, the molecular mechanisms of the anti-obesity effect of eight common spices are reviewed and evaluated in cell models, animal models and human subjects. Bioactive compounds from these spices are able to reduce lipid accumulation in fat cells and adipose tissues by regulating the expressions of related transcriptional factors such as CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ). They are also able to modulate the activities of certain enzymes related to lipogenesis, such as acyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FAS), glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) and others. After oral treatment with the spice extracts, apoptosis was induced in 3T3-L1 cells, thermogenesis was promoted in adipose tissues, and there was decreased body weight gain in obese animal models and human participants, which provide the basis for these functional food compounds to be developed into dietary supplements against obesity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...