A colon-specific delivery system for quercetin with enhanced cancer prevention based on co-axial electrospinning†
Abstract
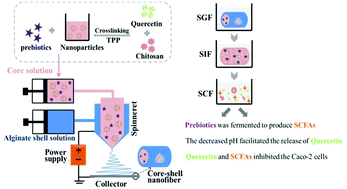
The antioxidant quercetin (Q) is a bioactive compound that can inhibit colon cancer. However, its poor stability in the upper gastro-intestinal tract and low bioavailability compromised its benefits. In this study, a biopolymer-based colon-specific delivery system for Q was constructed by co-axial electrospinning. Quercetin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles (QCNP) were firstly prepared and characterized. Then, a Q-loaded electrospun fiber mat (Q-loaded EFM) containing prebiotics (galactooligosaccharide, GOS) was fabricated using sodium alginate as the shell layer and the abovementioned QCNP and prebiotics as the core layer. The DPPH assay showed that the antioxidant activity of Q was maintained in the obtained film. Owing to the addition of prebiotic GOS, the obtained fiber mat exhibited good prebiotic effects. In vitro release kinetics showed a sustained and targeted colon-specific release of Q from the Q-loaded EFM containing GOS, and the release rate of Q was enhanced by the presence of GOS. The obtained film also exhibited inhibition effects on Caco-2 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy analysis indicated that the Q-loaded EFM containing GOS exerted its activity on colonic cancer cells by arresting the cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase and triggering apoptotic cell death. This study demonstrates the potential of the obtained film as an oral delivery system for encapsulation, protection, and release of Q at the colon for the oral therapy of colon disorders.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...