Deoxycholic acid disrupts the intestinal mucosal barrier and promotes intestinal tumorigenesis
Abstract
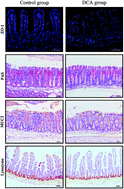
High-fat diet, which leads to an increased level of deoxycholic acid (DCA) in the intestine, is a major environmental factor in the development of colorectal cancer (CRC). However, evidence relating to bile acids and intestinal tumorigenesis remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the effects of DCA on the intestinal mucosal barrier and its impact on the development of CRC. Here we showed that DCA disrupted cell monolayer integrity and increased proinflammatory cytokine production in intestinal cancer and precancerous cell lines (Caco-2 and IMCE). Apcmin/+ mice receiving DCA increased the number and size of intestinal adenomas and promoted the adenoma–adenocarcinoma sequence. Importantly, DCA induced the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, increased the production of inflammatory cytokines, and led to intestinal low grade inflammation. A reduction of tight junction protein zonula occludens 1 (ZO-1) and the number of intestinal cells including goblet cells and Paneth cells was also observed after DCA treatment. Moreover, DCA significantly reduced the level of secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA), and promoted the polarization of M2 macrophages in the intestine of Apcmin/+ mice. In conclusion, these data suggested that DCA induced intestinal low grade inflammation and disrupted the mucosal physical and functional barriers, aggravating intestinal tumorigenesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...