Downregulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling with allicin for ameliorating the progression of osteoarthritis: in vitro and vivo studies
Abstract
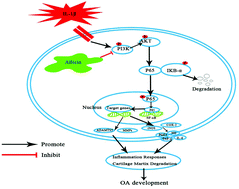
Osteoarthritis (OA) is characterized by the degeneration and destruction of articular cartilage. Allicin, a dietary garlic active constituent, exerts anti-inflammatory effects on several diseases. However, its effects on OA have not been clearly elucidated. In this study, we explored the effects of allicin on OA in both in vitro and in vivo models. Allicin inhibited interleukin-1β (IL-1β) induced overproduction of nitric oxide, inducible nitric oxide synthase, prostaglandin E2, and cyclooxygenase-2, as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in chondrocytes in a dose-dependent manner. Meanwhile, allicin reversed the overproduction of metalloproteinase-13 and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-5 and the decrease of aggrecan and type II collagen. Furthermore, allicin dramatically suppressed IL-1β-stimulated PI3K/Akt/NF-κB activation in chondrocytes. In vivo, treatment with allicin prevented the destruction of cartilage and inhibited PI3K/Akt/NF-κB activation in the cartilage of mice OA models. Taken together, these results indicate that allicin may be a potential therapeutic agent for OA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...