Lactobacillus plantarum LC27 and Bifidobacterium longum LC67 mitigate alcoholic steatosis in mice by inhibiting LPS-mediated NF-κB activation through restoration of the disturbed gut microbiota
Abstract
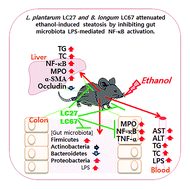
Long-term exposure to ethanol simultaneously causes gastrointestinal inflammation, liver injury, and steatosis. In the present study, we investigated the effects of Bifidobacterium longum LC67, Lactobacillus plantarum LC27, and their mixture (LM) against ethanol-induced steatosis in mice. Exposure to ethanol caused liver damage: it increased ALT, AST, TG, TC, and lipopolysaccharide levels in the blood and induced NF-κB activation in the liver. Oral administration of LC27, LC67, or LM in mice reduced ethanol-induced ALT, AST, TG, and TC levels in the blood and liver. These also suppressed ethanol-induced NF-κB activation and α-smooth muscle actin expression in the liver and increased ethanol-suppressed AMPK activation. Treatment with LC27, LC67, or LM increased ethanol-suppressed alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase activities in the liver, as well as tight junction protein expression in the liver and colon. Moreover, treatment with LC27, LC67, or LM restored the ethanol-disturbed gut microbiota composition, such as the increased population of Proteobacteria, and inhibited fecal and blood lipopolysaccharide levels. These inhibited NF-κB activation and increased tight junction protein expression in ethanol- or lipopolysaccharide-stimulated Caco-2 cells. These findings suggest that LC27, LC67, and LM can alleviate alcoholic steatosis by inhibiting LPS-mediated NF-κB activation through restoration of the disturbed gut microbiota.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...