Chitosan binding onto the epigallocatechin-loaded ferritin nanocage enhances its transport across Caco-2 cells†
Abstract
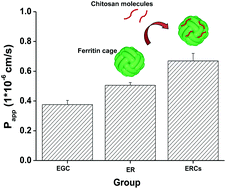
The effect of chitosan decoration on the transport of epigallocatechin (EGC)-encapsulated ferritin cage across the Caco-2 cells was investigated. After the encapsulation of EGC in apo-red bean (adzuki) ferritin (apoRBF), the EGC-loaded apoRBF nanoparticle (ER) was fabricated with an encapsulation ratio of 11.6% (w/w). The results indicated that different chitosan molecules (with molecular weights of 980, 4600, 46 000, and 210 000 Da) could attach onto the apoRBF via electrostatic interactions to form ER-chitosan complexes (ERCs) (ERCs980, ERCs4600, ERCs46000, and ERCs210000). ERCs980 and ERCs4600 retained the typical shell-like morphology of ferritin with a size distribution of 12 nm and showed weak negative zeta-potentials at pH 6.7, while ERCs46000 and ERCs210000 significantly aggregated. Furthermore, the transport of EGC in ERCs980 and ERCs4600 across the Caco-2 cells was enhanced by the transferrin receptor 1 (TfR-1)-mediated absorption pathway, demonstrating that chitosan molecules with low molecular weights of 980 and 4600 Da were beneficial to the absorption of EGC based on the ferritin cage. This study will facilitate the application of ferritin–chitosan materials for fabricating the core–shell platform for encapsulation and bioavailability enhancement of bioactive molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...