Monascin inhibits IL-1β induced catabolism in mouse chondrocytes and ameliorates murine osteoarthritis
Abstract
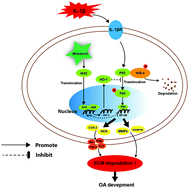
Osteoarthritis (OA) is an age-related degenerative disease and is the fourth major cause of disability, but there are no effective therapies because of its complex pathology and the side effects of the drugs. Previous research demonstrated that inflammation and ECM degradation play major roles in OA development. Monascin is an azaphilonoid pigment extracted from Monascus-fermented rice with a potential anti-inflammatory effect reported in various preclinical studies. In the present study, we investigated the protectiveness of monascin on interleukin (IL)-1β-induced mouse chondrocytes and surgical destabilization of the medial meniscus mouse (DMM) OA models. In vitro, monascin treatment inhibited the IL-1β-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). In addition, the IL-1β-stimulated matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) and thrombospondin motifs 5 (ADAMTS-5) upregulation and type two collagen and aggrecan degradation were reversed by monascin. Mechanistically, we revealed that monascin suppressed nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signalling by activating the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes. And monascin-induced protectiveness in OA development was also shown by using a DMM model. Altogether, our results suggested that monascin could be a novel therapeutic approach for OA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...