Dietary intake of glucono-δ-lactone attenuates skin inflammation and contributes to maintaining skin condition
Abstract
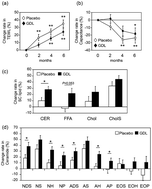
Skin properties are influenced by both external (e.g., ultraviolet [UV], chemicals, and bacteria) and internal factors (e.g., nutrition and hormones). Therefore, some dietary supplements are expected to improve skin conditions. Glucono-δ-lactone (GDL) is widely used as a food additive and is naturally present in wine, honey, and other foods. The aim of this study was to assess whether GDL improves skin condition and inflammation. In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 40 healthy Japanese male volunteers were randomly assigned to either the GDL (2000 mg day−1) or placebo group. A significant difference was found in the rates of change in transepidermal water loss (TEWL) from the baseline to 6 months between the placebo and GDL groups (P < 0.05). Facial lightness (L*) significantly increased by 1.6% only in the GDL group at 6 months compared with the baseline. The value of the elasticity parameter, Ua/Uf, of dietary GDL significantly increased (6.2% at 2 months and 5.4% at 6 months). Besides these, dietary GDL suppressed UVB-induced erythema (a*) and pigmentation (L*). Dietary GDL has anti-inflammatory effects on the skin and prevents/improves skin disorders caused by seasonal change.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...