Interactions of flavonoids with α-amylase and starch slowing down its digestion
Abstract
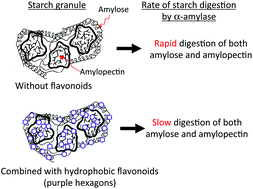
Starch is digested to glucose in the intestine and absorbed into the body. If the increased blood concentrations of sugar after meals decrease slowly or are maintained for a long time, various adverse effects are induced. Therefore, it is important to decrease the rate of the digestibility of starch in the intestine in the patients of hyperglycemia. One of the ways to effect a decrease is the inhibition of α-amylase secreted from the pancreas. Flavonoids are a group of compounds that can inhibit this enzyme's activity, and many investigators have studied the flavonoid-dependent inhibition of this enzyme and presented mechanisms for the inhibition of its activity. Starch containing foods, however, cooked or ingested with flavonoid containing foods are mixed with saliva and gastric juice in the stomach. Thus, flavonoids in the foods can interact with starch and can react with nitrous acid derived from the oral cavity in the stomach before being transported to the intestine. This review mainly deals with: (i) the inhibition of α-amylase activity by flavonoids suggesting the mechanisms of the inhibition, (ii) suppression of starch digestion by flavonoids by forming starch–flavonoid complexes by hydrophobic interactions, and (iii) formation of starch not easily digested by α-amylase by the formation of covalent bonds between flavonoids and starch during cooking and in the stomach. In addition, the cooperation of flavonoids with fatty acids are discussed taking their binding to amylose into account.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...