Asiatic acid suppresses neuroinflammation in BV2 microglia via modulation of the Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
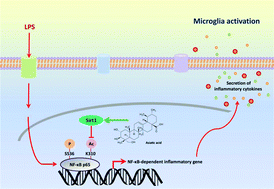
Asiatic acid, a triterpenoid derived from Centella asiatica, has been found to exhibit multiple bioactivities. In this study, we investigated the effects of asiatic acid on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation and explored the mechanism of its action in BV2 microglia. We found that asiatic acid (0.1 to 100 μM) treatment significantly attenuated nitric oxide (NO) production and inhibited inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in a concentration-dependent manner following LPS exposure. Asiatic acid reduced LPS-induced expression and secretion of inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in BV2 cells. In addition, asiatic acid enhanced Sirt1 expression, reduced NF-κB p65 acetylation, and suppressed NF-κB activation after LPS stimulation. However, EX-527, an inhibitor of Sirt1, abolished the inhibitory effects of asiatic acid on LPS-stimulated microglia activation. These findings suggest that asiatic acid prevents LPS-induced neuroinflammation via regulating the Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...