Structural elucidation and immunostimulatory activity of a new polysaccharide from Cordyceps militaris
Abstract
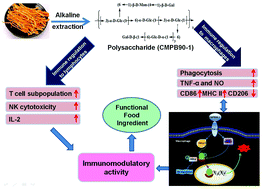
A new polysaccharide (CMPB90-1) was isolated from cultured Cordyceps militaris by alkaline extraction. The chemical structure of CMPB90-1 was determined by analysis of physicochemical and spectral data. The backbone of CMPB90-1 is composed of (1→6)-linked α-D-glucopyranosyl and (1→3)-linked α-D-glucopyranosyl residues, with branching at O-6, which consists of (1→4)-linked β-D-mannopyranosyl and (1→6)-linked α-D-glucopyranosyl residues, respectively. β-D-Galactopyranosyl residues is the terminal unit. In vitro immunomodulatory assay revealed that CMPB90-1 promoted proliferation of splenic lymphocytes, enhanced cytotoxicity of NK cells and promoted lymphocyte secretion of the cytokine interleukin-2. Besides, CMPB90-1 upregulated T-cell subpopulation, strengthened phagocytosis function of macrophages and induced their M1 polarization. The mechanism of the effects might be due to the activation of TLR2, MAPK and NF-κB pathways. The results proposed that CMPB90-1 can be researched and developed as a new functional food.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function 2018 Most Downloaded Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...