G4-quartet hydrogels from 5′-hydrazino-guanosine for the non-covalent and covalent remediation of contaminants from water†
Abstract
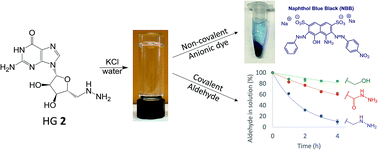
The creation of supramolecular hydrogels from relatively simple building blocks demonstrates the power of molecular self-assembly to make functional materials. G4-quartet hydrogels are appealing for a number of applications, including the environmental remediation of pollutants in water. We find that the guanosine analog, 5′-deoxy-5′-hydrazinoguanosine (HG 2) self-assembles into a self-standing hydrogel in the presence of stoichiometric amounts (0.25 equiv.) of KCl. The higher water solubility of HG 2 (14.5 mM), compared to that of the parent compound G 1 (2.1 mM), likely contributes to its enhanced gelation. The structural basis for this HG 2·KCl hydrogel, confirmed by PXRD, IR and CD, is the G4·K+ quartet, which forms extended 1D ion-channel assemblies that entangle to give a stable and long-lived hydrogel. We also find that adding KCl to a saturated solution of HG 2 triggers the generation of colloidal G4·K+ assemblies in situ that selectively and efficiently binds the anionic dye naphthol blue black (NBB) over a cationic dye. In addition to this non-covalent electrostatic binding of anions, the nucleophilic 5′-hydrazino group in the HG 2·KCl hydrogel HG 2 enables the efficient absorption of propionaldehyde from both the gas phase and from water solution via the formation of covalent hydrazone linkages with the gel matrix.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Artificial Water Channels


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...