No effect of selected engineered nanomaterials on reproduction and survival of the springtail Folsomia candida†
Abstract
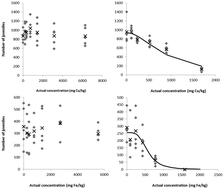
Although the number of studies on engineered nanomaterial (NM) toxicity to soil invertebrates is increasing, only a few studies have reported toxicity of NMs to soil dwelling model species, such as the invertebrate Folsomia candida. The main objective of this study was to determine the toxicity of five different engineered NMs (WCCo, CuO, Fe2O3, organic pigment and MWCNTs) for the springtail F. candida. Copper(II), cobalt and iron chlorides were taken as positive controls. A standardized OECD test was used to measure effects on reproduction and survival, and toxicity was related to metal concentrations in soil and pore water. None of the NMs exerted adverse effects on springtail reproduction and survival at concentrations up to 6400 mg per kg dry soil, whereas the Cu, Co and Fe chlorides resulted in 50% decline in springtail reproduction at 981, 469 and 569 mg metal ion per kg dry soil, respectively. The absence of toxicity of the NMs could partly be explained by the low porewater metal concentrations, suggesting low solubility or slow solubilisation. The fate of engineered NMs in soil is rather complex but needs better understanding to facilitate predicting exposure of soil organisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...