Cadmium-free CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots as efficient and robust photosensitizers in combination with a molecular catalyst for visible light-driven H2 production in water†
Abstract
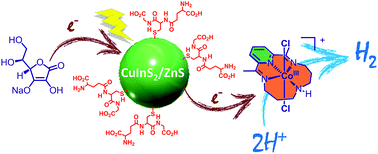
We demonstrate that cadmium-free core–shell CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) are very efficient and robust visible-light absorbing photosensitizers for photocatalytic hydrogen production in a fully aqueous solution when associated with a molecular catalyst, a cobalt tetraazamacrocyclic complex. In the presence of ascorbate as a sacrificial electron donor, this new hybrid system exhibits a remarkable activity for hydrogen production under visible light irradiation at pH 5.0 with up to 7700 and 1010 turnover numbers versus catalyst and QDs, respectively, and with an initial turnover frequency per QD of 1.59 mmolH2 gQD−1 h−1. These are the best performances reported so far with cadmium-free QDs in combination with a molecular catalyst, highlighting the great potential of ternary chalcopyrite nanocrystals as efficient and robust materials for solar fuel production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...