Designed single-source precursors for iron germanide nanoparticles: colloidal synthesis and magnetic properties†
Abstract
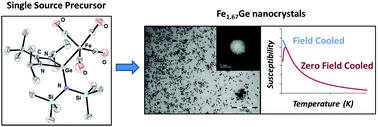
The synthesis of iron germanide nanoparticles at the nanoscale is a challenging task. Here, we describe the preparation of nanocrystals of the hexagonal Fe1.67Ge phase via the thermolysis of single source precursors [{iPrNC(tBu)NiPr}RGe]Fe(CO)4 (where R = Cl, N(SiMe3)2) under mild conditions (200 °C). These bimetallic precursors and the corresponding germylenes [{iPrNC(tBu)NiPr}RGe] were fully characterized by spectroscopic techniques as well as single crystal X-ray diffraction. While the structural features of the molecular species were shown to be almost identical, the results of the thermolysis were highly dependent on the nature of R. When R = Cl, multimodal size distributions and non-controlled phases were obtained. In contrast, the thermolysis of [{iPrNC(tBu)NiPr}{N(SiMe3)2}Ge]Fe(CO)4 yielded pure ferromagnetic Fe1.67Ge nanoparticles with a mean diameter close to 6 nm and a narrow size distribution (<12%). These results were rationalized in terms of Ge–substituent bond energy thanks to a computational study.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...